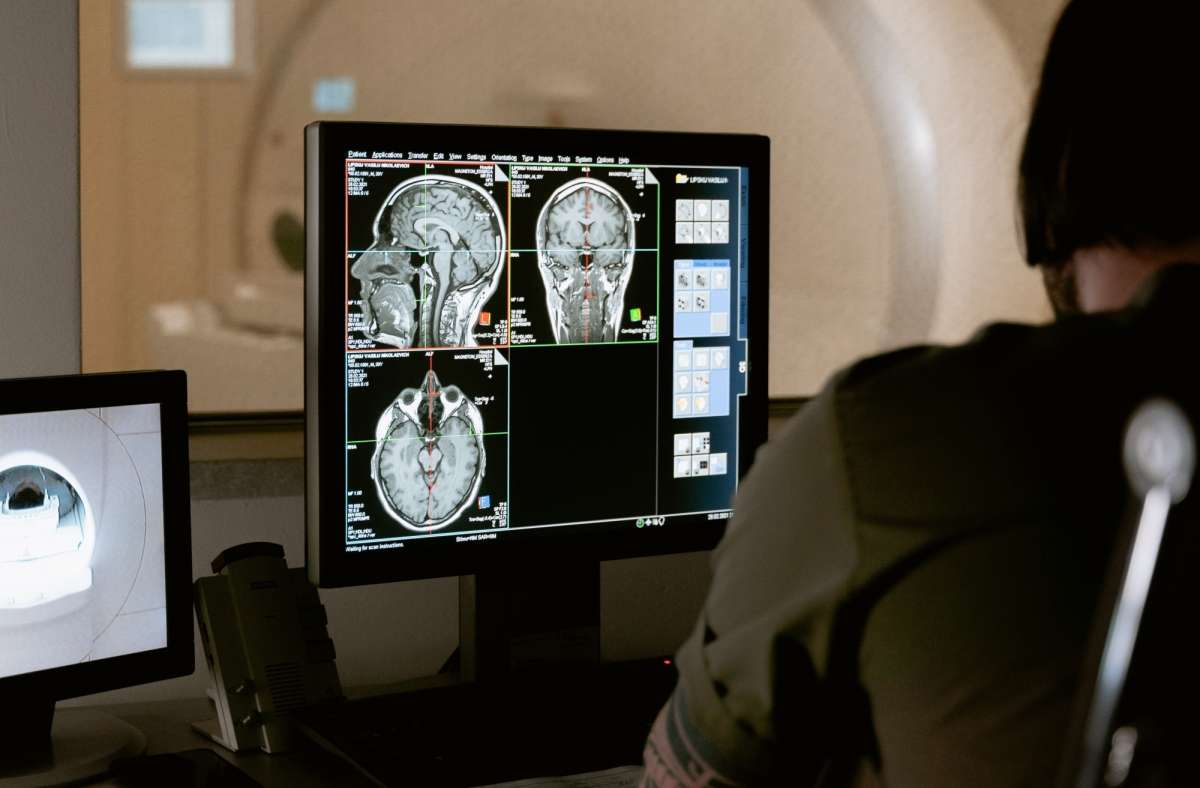
The fMRI scans are commonly used to non-invasively map brain connectivity in a variety of situations, including planning for surgery, understanding the impact of a stroke, and studying how mental illness affects neurological function…reports Asian Lite News
Some brain scans can give false readings as people tend to become more relaxed and sleepy and changes in breathing and heart rates alter blood oxygen levels in the brain — which are then falsely detected on the scan as normal neuronal activity, a new study showed on Wednesday.
The tendency of people’s arousal to wane over the course of brain scans has been distorting the brain connection maps produced by functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), said investigators from McLean Hospital (a member of Mass General Brigham), Harvard Medical School and the National Institute on Drug Abuse – Intramural Research Programme (NIDA-IRP) in the US.
“These arousal-dampening conditions create the illusion that people’s brain connection strengths continuously inflate throughout the scan to help better connect the ideas,” said Cole Korponay, a Research Fellow at the McLean Hospital Imaging Center, in the study published in the journal Nature Human Behaviour.
The fMRI scans are commonly used to non-invasively map brain connectivity in a variety of situations, including planning for surgery, understanding the impact of a stroke, and studying how mental illness affects neurological function.
However, since fMRI relies on changes in brain blood oxygen to indirectly measure neuronal activity, it is vulnerable to “noise” from other processes that can affect blood oxygen – such as changes in breathing and heart rates.
Since breathing and heart rate patterns are closely tied to arousal levels, changes in arousal can introduce significant noise into fMRI data.
In the study, the research team identified a specific blood flow signal that seemed to track both the decline in subject arousal levels and the illusory inflation of functional brain connection strengths.
This non-neuronal, physiological noise signal – termed the “systemic low frequency oscillation” (sLFO) signal – grew over time during scanning, that tightly matched the pattern of the connection strength increases.
“By adopting this sLFO denoising procedure, future studies can mitigate the distortive effects of arousal changes during brain scans and enhance the validity and reliability of fMRI findings,” said Korponay.